 Login
Now
Login
Now
 Login
Now
Login
Now
Get started with our seamless hosting process in just a few simple steps
Choose your miner and hosting plan
Place an order
Receive updates about install
Connect your wallet
Start mining
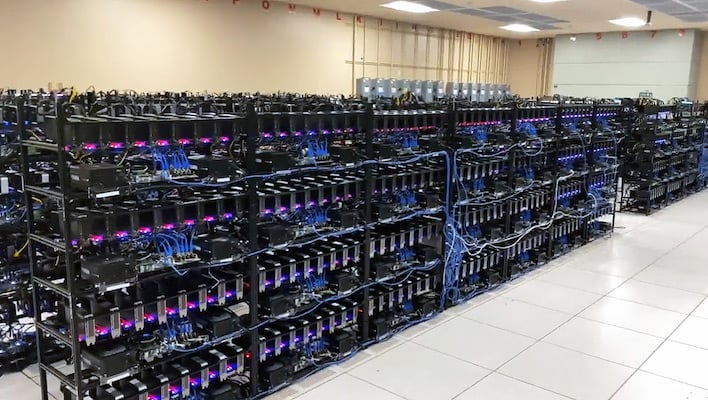
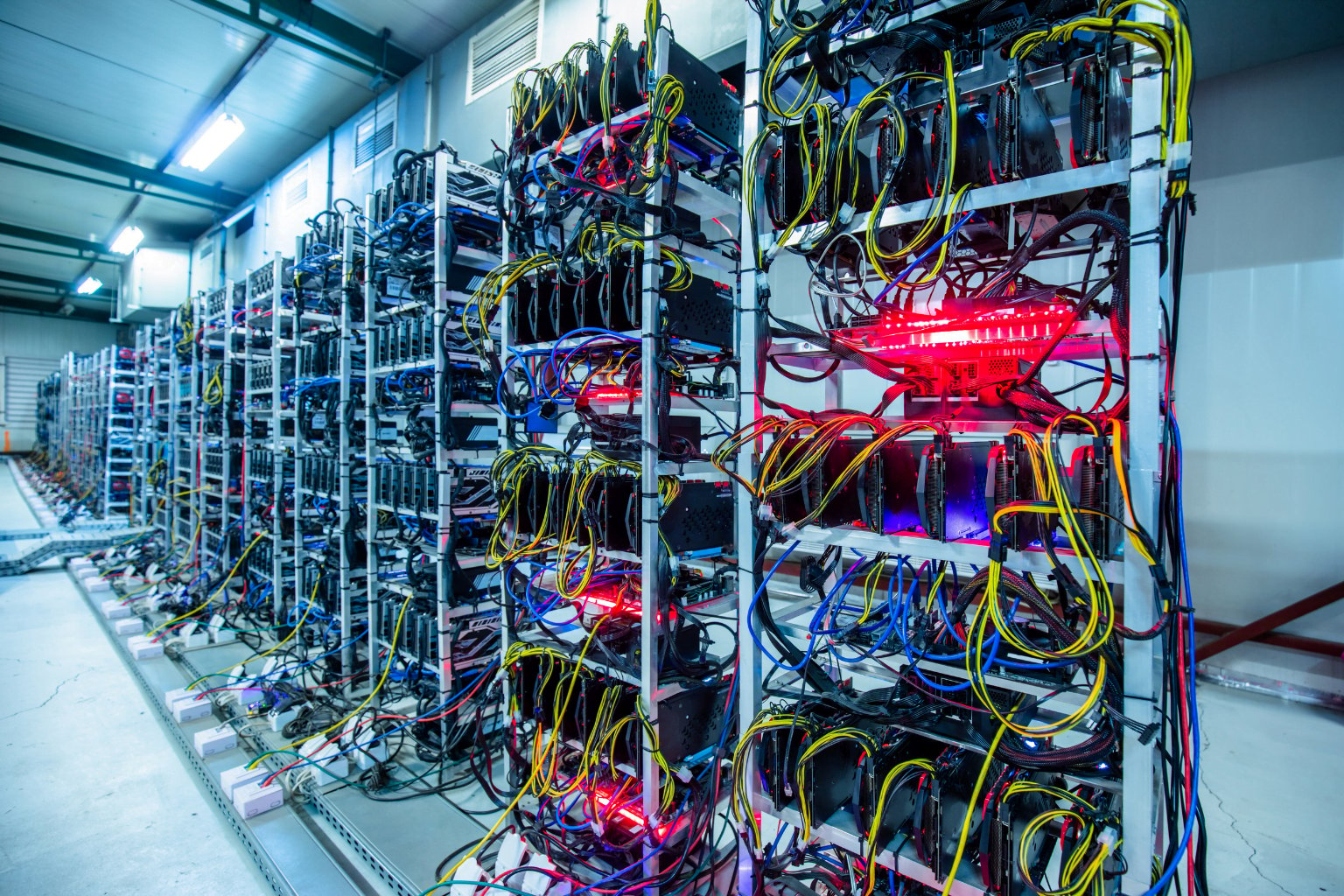
State-of-the-art facilities with industry-leading uptime and security
total site capacity
guaranteed uptime
available hosting space
Min Req
on-site support



Have questions about our crypto farming services? Reach out and we'll connect with you within 24 hours.
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are entered into circulation and transactions are verified on the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems that validate transaction blocks. The first miner to solve the problem gets to add the block to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees.
As of 2023, the Bitcoin block reward is 6.25 BTC per block. This reward halves approximately every four years in an event called "the halving." The next halving is expected in 2024, which will reduce the block reward to 3.125 BTC.
Mining difficulty is a measure of how hard it is to find a new block compared to the easiest it can ever be. The Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty approximately every two weeks to maintain a consistent block time of 10 minutes. Higher difficulty means more computational power is required to mine Bitcoin, which can reduce profitability as energy costs increase relative to potential rewards.
Solo mining involves mining Bitcoin independently without joining a group. While you keep the full block reward if you successfully mine a block, the chances of doing so are extremely low without massive computational power. Pool mining involves combining resources with other miners to increase the chances of finding blocks. Rewards are then distributed among pool members based on their contributed hash power, providing more consistent, though smaller, earnings.
Proof of Work (PoW) is the consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies, where miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks. Proof of Stake (PoS) is an alternative consensus mechanism where validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they "stake" or lock up as collateral. PoS is generally more energy-efficient but has different security considerations compared to PoW.
Bitcoin mining consumes a significant amount of electricity, estimated to be comparable to the energy usage of medium-sized countries. However, it's important to note that a growing percentage of Bitcoin mining uses renewable energy sources. Many mining operations are located near renewable energy sources or utilize excess energy that would otherwise be wasted.
Cloud mining allows individuals to participate in cryptocurrency mining without owning or maintaining hardware. Users lease mining power from companies that operate large-scale mining facilities. Profitability depends on several factors including Bitcoin's price, mining difficulty, maintenance fees, and the cloud mining contract terms. While it eliminates hardware costs and technical barriers, users should carefully research providers as the industry has seen its share of scams.
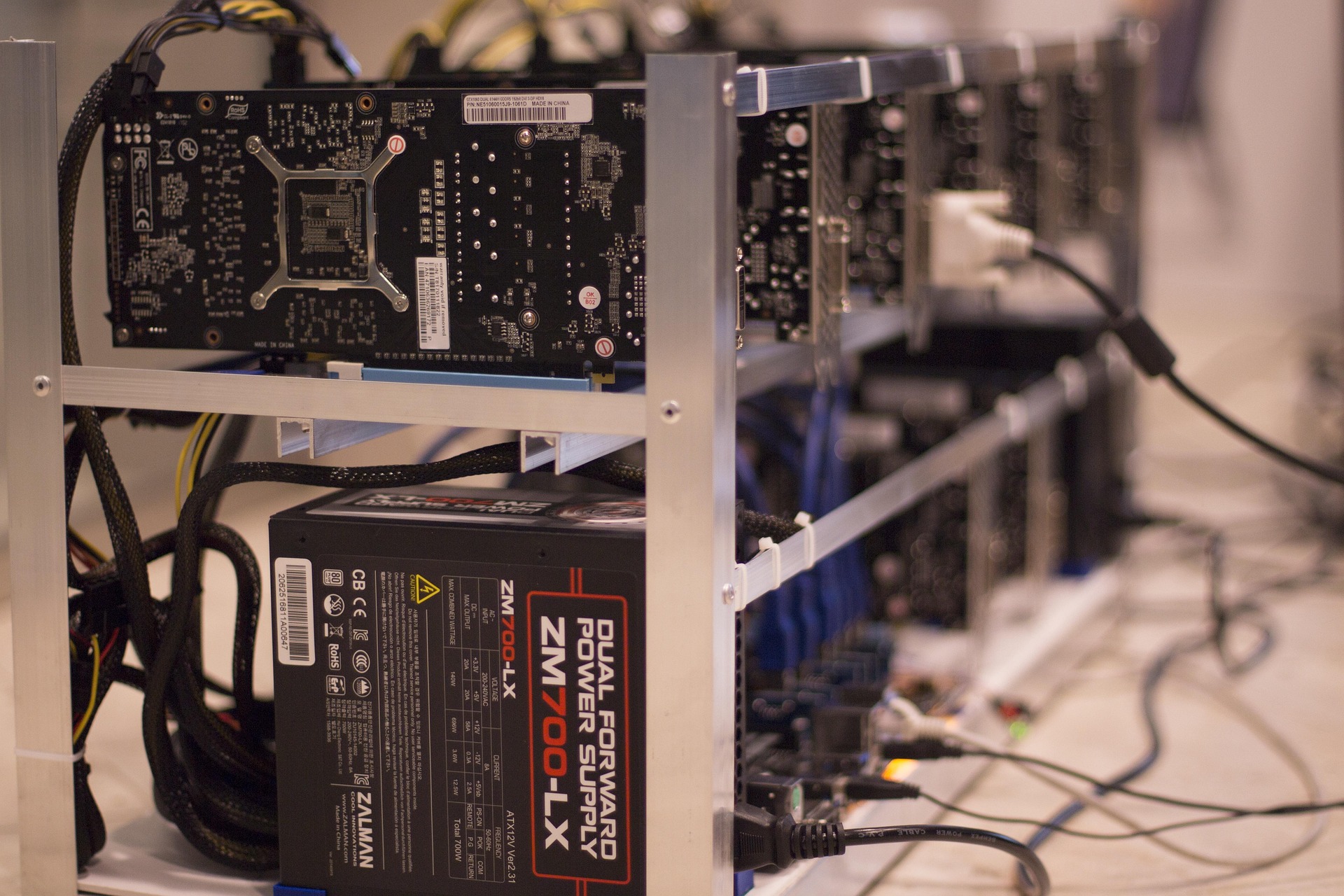
ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners are specialized hardware designed exclusively for cryptocurrency mining. Unlike general-purpose CPUs or GPUs, ASICs are optimized for the specific algorithms used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (SHA-256). They are significantly more efficient and powerful than alternative mining hardware, which is why they dominate the Bitcoin mining industry today.
There's no fixed time to mine one Bitcoin as it depends on multiple factors including your mining hardware's hash rate, the total network hash rate, mining difficulty, and whether you're mining solo or in a pool. With the current network difficulty, it would take a single average ASIC miner several years to mine one complete Bitcoin. Most individual miners join pools to receive smaller, more frequent rewards proportional to their contributed hash power.
Bitcoin mining profitability for individuals depends on several factors: electricity costs (the most significant expense), efficiency of mining hardware, Bitcoin's market price, and network difficulty. In regions with very low electricity costs, individual mining can still be profitable. However, for most people in areas with average or high electricity rates, joining a mining pool or considering cloud mining options may be more viable than solo mining. Always use a mining profitability calculator before investing in equipment.
When all 21 million Bitcoins are mined (expected around the year 2140), miners will no longer receive block rewards in the form of new Bitcoins. Instead, they will earn income solely from transaction fees. The Bitcoin protocol is designed to continue operating on this fee-based model, incentivizing miners to continue securing the network by processing and validating transactions.
While it was possible to mine Bitcoin with CPUs and GPUs in the early years, today it is not economically feasible. The Bitcoin network difficulty has increased to a point where specialized ASIC miners are millions of times more efficient than general-purpose hardware. Attempting to mine Bitcoin with a CPU or GPU would likely result in earning less than a penny worth of Bitcoin while spending significantly more on electricity. GPUs remain viable for mining some other cryptocurrencies with different algorithms.